[fusion_builder_container hundred_percent=”no” equal_height_columns=”no” menu_anchor=”” hide_on_mobile=”small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility” class=”” id=”” background_color=”” background_image=”” background_position=”center center” background_repeat=”no-repeat” fade=”no” background_parallax=”none” parallax_speed=”0.3″ video_mp4=”” video_webm=”” video_ogv=”” video_url=”” video_aspect_ratio=”16:9″ video_loop=”yes” video_mute=”yes” overlay_color=”” video_preview_image=”” border_size=”” border_color=”” border_style=”solid” padding_top=”” padding_bottom=”” padding_left=”” padding_right=””][fusion_builder_row][fusion_builder_column type=”1_1″ layout=”1_1″ background_position=”left top” background_color=”” border_size=”” border_color=”” border_style=”solid” border_position=”all” spacing=”yes” background_image=”” background_repeat=”no-repeat” padding_top=”” padding_right=”” padding_bottom=”” padding_left=”” margin_top=”0px” margin_bottom=”0px” class=”” id=”” animation_type=”” animation_speed=”0.3″ animation_direction=”left” hide_on_mobile=”small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility” center_content=”no” last=”no” min_height=”” hover_type=”none” link=””][fusion_text columns=”” column_min_width=”” column_spacing=”” rule_style=”default” rule_size=”” rule_color=”” hide_on_mobile=”small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility” class=”” id=””]
Welcome to “How To Understand Your Equifax Repayment History Information“
in the MyCRA (Specialist Credit Repair) Lawyers “Did You Know” Series.
This series of Hints, Tips, and (Legislation) Snippets will Reveal The Truth behind Credit Reporting Legislation, Privacy Legislation and Credit Repair.
You will discover:
- ways you can help your clients (without the need to engage us)
- ways clients can help themselves
- Pitfalls to avoid
Tip 102 (Credit Reporting Bodies)
They say knowledge is power but I believe the true power is in applying that knowledge.
How To Understand Your Equifax Repayment History Information (RHI) in 2019
Quick Background (condensed)
- March 2014 saw the introduction of Repayment History Information (RHI) within the Privacy Act (1988)
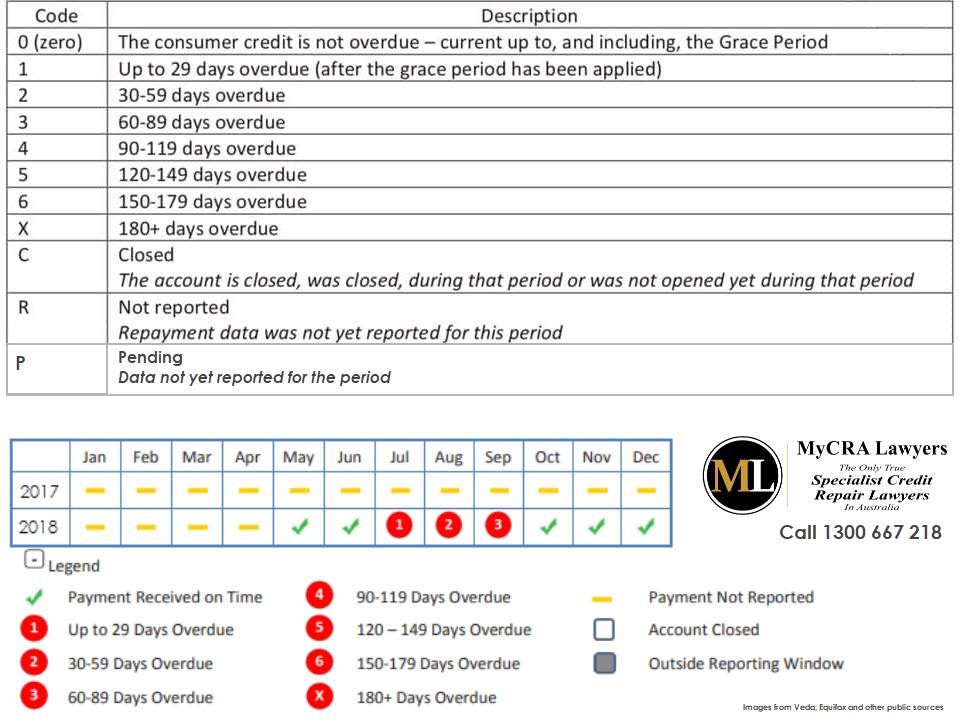
- Information to be recorded when you pay your bills more than 14 days late
- July 2018 saw legislation to force Licensed Credit Providers (LCP) to supply RHI
Proposed Purpose
- Offer greater transparency as to the creditworthiness of individuals
- Reduce LCP [new client] risk by identifying consistent slow payers
- Offer lower rates and better terms to individuals that pay on time
- A slight reduction in credit score
Anecdotal Result (to date)
- Inconsistent information being provided by LCP to Equifax (and others)
- RHI alone being the cause of Home Loan / Finance declines
- Significant reduction in credit scores
- Confusion over how to understand the RHI tables
I have included a table below (which is a slightly modified version and a combination of data published by Equifax and others), explaining how to understand your Equifax Repayment History Information (RHI) in 2019.
Please comment below if you have additional information about RHI that you think will help.
What Now?
If your Credit Rating is polluted with black marks, and if those black marks (Judgments, Defaults, Enquiries) are the reason you can’t get finance, and if your life would be easier (and better) with a clean, sparkling, and shiny credit file you can be proud of, then you deserve a second chance, don’t you?
If you do deserve a second chance, call MyCRA Lawyers now on 1300 667 218
(Mention this particular post for a Free Initial Consultation (Valued at up to $440) with our Specialist Credit Repair Lawyers or their assistants.)
Click HERE or more in this “Did You Know” series
Here’s a little more Info, Case Studies, and Reviews etc.
Click here to check out a few more reviews like…
[ Just in case the link above doesn’t work, copy and paste it into your browser
https://www.ekomi.co.uk/review-fc055e2cb9baab91cc850f5c7ae05c29.html ]
and check out our Google Reviews











Actual Credit Repair Case Studies
Have a look at a few previous success stories (Case Studies), and once you’ve made the decision to call us now on 1300 667 218,
we’ll step you through our unique systems and processes (all designed to make it stress-free and easy for you), so you can get started today too…
*************************************
[/fusion_text][/fusion_builder_column][/fusion_builder_row][/fusion_builder_container]